DCS293 - High Performance Computing 2021 Fall
前言
本文通过 NVDIA 的矩阵计算函数库 cuBLAS 计算矩阵相乘,并进行性能比较与分析;使用滑窗法和在 GPU 上进行直接卷积和 im2col 方法卷积;使用 cuDNN 进行卷积并比较性能。
实验环境
Linux jupyter-zhamao 5.4.0-74-generic #83~18.04.1-Ubuntu SMP
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6242 CPU @ 2.80GHz 16 cores 32 processors
NVIDIA Tesla V100-SXM2-32GB × 4
- Driver Version: 440.33.0
- CUDA Version: 10.2
cuBLAS
cuBLAS 在 CUDA6.0 中出现,现在包含2个类 API,常规 cuBLAS,简称为 cuBLAS API,另外一种是 CUBLASXT API。使用 cuBLAS 的时候,应用程序应该分配矩阵或向量所需的 GPU 内存空间,并加载数据,调用所需的 cuBLAS 函数,然后从 GPU 的内存空间上传计算结果至主机,cuBLAS API 也提供一些帮助函数来从 GPU 中写或者读取数据。
通过 NVDIA 的矩阵计算函数库 cuBLAS 计算矩阵相乘,矩阵规模从512增加至8192。
cuBLAS 默认按照列优先原则存储矩阵。根据 $(B^TA^T)^T = AB$ 我们对输入和计算结果进行转置即可。但是我发现他的函数里面已经可以通过参数控制是否转置 A 和 B,还是很厉害的。
cuBLAS中能用于运算矩阵乘法的函数有4个,分别是 cublasSgemm(单精度实数)、cublasDgemm(双精度实数)、cublasCgemm(单精度复数)、cublasZgemm(双精度复数)。这里使用 cublasSgemm ,它的定义(在 cublas_v2.h 和 cublas_api.h 中)如下。
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
#define cublasSgemm cublasSgemm_v2
CUBLASAPI cublasStatus_t CUBLASWINAPI cublasSgemm_v2
(
cublasHandle_t handle,
cublasOperation_t transa, cublasOperation_t transb,
int m, int n, int k,
const float *alpha,
const float *A, int lda,
const float *B, int ldb,
const float *beta,
float *C, int ldc
);
该函数实际上是用于计算 C = α A B +β C 的,其中 $A_{m×k}$ 、$B_{k×n}$ 、$C_{m×n}$ 为矩阵,α 、β 为标量。在此处 α = 1,β = 0.
首先需要使用 cuBLAS 库
0
#include <cublas_v2.h>
下面初始化三个矩阵和先前的代码相同,把矩阵发给设备和计算如下:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
cublasHandle_t handle;
cublasStatus_t status = cublasCreate(&handle);
if (status != CUBLAS_STATUS_SUCCESS) {
if (status == CUBLAS_STATUS_NOT_INITIALIZED) {
printf("cuBLAS 对象实例化出错\n");
}
getchar();
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
float *cuda_A, *cuda_B, *cuda_C;
cudaMalloc((void **)&cuda_A, sizeof(float) * MATRIX_SIZE * MATRIX_SIZE);
cudaMalloc((void **)&cuda_B, sizeof(float) * MATRIX_SIZE * MATRIX_SIZE);
cudaMalloc((void **)&cuda_C, sizeof(float) * MATRIX_SIZE * MATRIX_SIZE);
cublasSetVector(
MATRIX_SIZE * MATRIX_SIZE, // 要存入显存的元素个数
sizeof(float), // 每个元素大小
A, // 主机端起始地址
1, // 连续元素之间的存储间隔
cuda_A, // GPU 端起始地址
1 // 连续元素之间的存储间隔
);
cublasSetVector(
MATRIX_SIZE * MATRIX_SIZE, // 要存入显存的元素个数
sizeof(float), // 每个元素大小
B, // 主机端起始地址
1, // 连续元素之间的存储间隔
cuda_B, // GPU 端起始地址
1 // 连续元素之间的存储间隔
);
// 同步函数
// cudaError_t cudaThreadSynchronize() is deprecated [-Wdeprecated-declarations]
// cudaThreadSynchronize();
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
float alpha = 1;
float beta = 0;
cublasSgemm(
handle, // blas 库对象
CUBLAS_OP_T, // 矩阵 A 属性参数
CUBLAS_OP_T, // 矩阵 B 属性参数
MATRIX_SIZE, // A, C 的行数
MATRIX_SIZE, // B, C 的列数
MATRIX_SIZE, // A 的列数和 B 的行数
&alpha, // 运算式的 α 值
cuda_A, // A 在显存中的地址
MATRIX_SIZE, // lda
cuda_B, // B 在显存中的地址
MATRIX_SIZE, // ldb
&beta, // 运算式的 β 值
cuda_C, // C 在显存中的地址(结果矩阵)
MATRIX_SIZE // ldc
);
// 同步函数
// cudaThreadSynchronize();
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
cublasGetVector(
MATRIX_SIZE * MATRIX_SIZE, // 要取出元素的个数
sizeof(float), // 每个元素大小
cuda_C, // GPU 端起始地址
1, // 连续元素之间的存储间隔
C, // 主机端起始地址
1 // 连续元素之间的存储间隔
);
clock_t endTime = clock();
// C^T
cToR(C, MATRIX_SIZE, MATRIX_SIZE);
clock_t endTime2 = clock();
cudaThreadSynchronize() 建议换成 cudaDeviceSynchronize()
编译记得加上 -lcublas
| MatrixSize | Time [转置后(转置前)] | blockSize = 32 | blockSize = 512 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 512 | 0.444934s (0.440606s) | 0.2052s | 0.2213s |
| 1024 | 0.483945s (0.467051s) | 0.2137s | 0.2214s |
| 2048 | 0.625998s (0.518511s) | 0.2380s | 0.2356s |
| 4096 | 0.979877s (0.536048s) | 0.4239s | 0.3105s |
| 8192 | 3.677618s (1.129133s) | 1.4426s | 0.4903s |
CUBLAS 可能转置 A 和 B 有一定开销,所以就算结果不经过转置也比任务1的实现慢许多。
尝试不转置 A 和 B 把 CUBLAS_OP_T 改为 CUBLAS_OP_N。
不转置的话确实快一点。但是还是比 block size = 512 的要慢。我写的程序在访存的时候显然没有使用共享内存,时延较高,但是却和 cublas 不相上下甚至比它快。可能是显卡性能强劲的原因。
CUDA CNN
在信号处理、图像处理和其他工程/科学领域,卷积是一种使用广泛的技术。在深度学习领域,卷积神经网络(CNN)这种模型架构就得名于这种技术。在本实验中,我将在 GPU 上实现卷积操作,注意这里的卷积是指神经网络中的卷积操作,与信号处理领域中的卷积操作不同,它不需要对 Filter 进行翻转,不考虑 bias。
通过CUDA实现直接卷积(滑窗法),输入从256增加至4096或者输入从32增加至512.
输入:Input和Kernel(3x3)
问题描述:用直接卷积的方式对Input进行卷积,这里只需要实现2D, height*width,通道channel(depth)设置为3,Kernel (Filter)大小设置为3*3*3,个数为3,步幅(stride)分别设置为1,2,3,可能需要通过填充(padding)配合步幅(stride)完成CNN操作。注:实验的卷积操作不需要考虑bias(b),bias设置为0.
输出:输出卷积结果以及计算时间
对于结果矩阵中的每一个位置创建一个线程与之计算对应,并且为了防止产生数据依赖,每个线程需要将位置的所有 Chanel 中需要累加的值完全计算,得出完整的值。
首先我们还是一个处理单元计算输出矩阵的一个元素。根据输入矩阵和滤波器参数来确定补0和输出矩阵大小。

0
1
2
3
4
5
6
const int zeroPadding = (FILTER_SIZE - 1) / 2;
const int in2DSize = MATRIX_SIZE + 2 * zeroPadding;
const int out2DSize = (MATRIX_SIZE - FILTER_SIZE + 2 * zeroPadding) / STRIDE + 1;
dim3 blockSize(BLOCK_SIZE, BLOCK_SIZE);
dim3 gridSize((out2DSize + blockSize.x - 1) / blockSize.x,
(out2DSize + blockSize.y - 1) / blockSize.y);
然后申请矩阵空间,与任务一相似。
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
float *hInMat = (float *)malloc(sizeof(float) * MATRIX_CHANNEL * in2DSize * in2DSize);
float *hKernel = (float *)malloc(sizeof(float) * MATRIX_CHANNEL * FILTER_SIZE * FILTER_SIZE);
float *hOutMat = (float *)malloc(sizeof(float) * MATRIX_CHANNEL * out2DSize * out2DSize);
srand(0);
for (int d = 0; d < MATRIX_CHANNEL; d++) {
for (int i = zeroPadding; i < in2DSize - zeroPadding; i++) {
for (int j = zeroPadding; j < in2DSize - zeroPadding; j++) {
hInMat[d * in2DSize * in2DSize + i * in2DSize + j] = (float)rand() / RAND_MAX;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < MATRIX_CHANNEL * FILTER_SIZE * FILTER_SIZE; i++) {
hKernel[i] = (float)rand() / RAND_MAX;
}
开始计时,申请设备上显存空间然后把数据复制过去。代码省略。
然后开始计算卷积。
0
1
2
3
4
5
CONV2D<<<gridSize, blockSize, 0>>>
(dInMat, dKernel, dOutMat,
in2DSize, out2DSize,
MATRIX_CHANNEL,
FILTER_NUM, FILTER_SIZE,
STRIDE, zeroPadding);
核函数如下:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
// CUDA kernel function
__global__
void CONV2D(const float *input, const float *kernel, float *output, const int in2DSize, const int out2DSize, const int depth, const int K, const int f, const int stride, const int zeroPadding) {
const int row = threadIdx.y + blockIdx.y * blockDim.y;
const int col = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;
if (row < out2DSize && col < out2DSize) {
for (int c = 0; c < depth; c++) {
output[idx(c, row, col, out2DSize)] = 0.0f;
int x = row * stride;
int y = col * stride;
for (int k = 0; k < K; k++) {
for (int i = 0; i < f; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < f; j++) {
output[idx(c, row, col, out2DSize)] += input[idx(k, x + i, y + j, in2DSize)] * kernel[idx(k, i, j, f)];
}
}
}
}
}
return;
}
| MatrixSize | Time [S = 1] | Time [S = 2] | Time [S = 3] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 512 | 0.207790s | 0.215431s | 0.210600s |
| 1024 | 0.224814s | 0.218759s | 0.217814s |
| 2048 | 0.309920s | 0.296813s | 0.225991s |
| 4096 | 0.451333s | 0.367948s | 0.318341s |
| 8192 | 0.913531s | 0.574979s | 0.521228s |
使用 im2col 方法结合 GEMM 实现卷积操作
用im2col的方式对Input进行卷积,这里只需要实现2D, height*width,通道channel(depth)设置为3,Kernel (Filter)大小设置为3*3*3,个数为3。
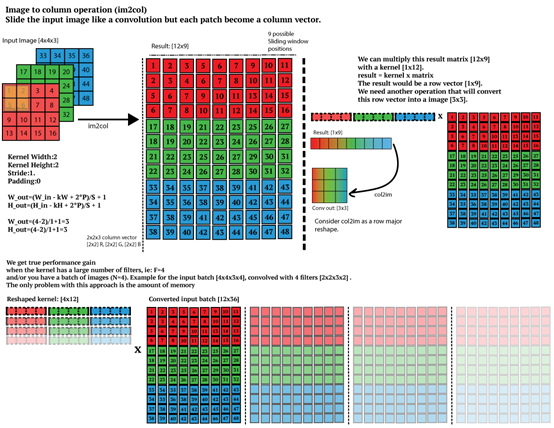
根据步长、卷积核大小等信息将输入矩阵由3D转换为2D,将卷积核变成一维向量。数个卷积核向量拼成矩阵与输入矩阵Matrix(2D)相乘,即可得到结果。
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
// im2col
// Mat3D2Mat2D
dx[9] = {-1, 0, 1, -1, 0, 1, -1, 0, 1};
dy[9] = {-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1};
for (int d = 0; d < MATRIX_CHANNEL; d++) {
for (int i = 0; i < in2DSize; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < in2DSize; j++) {
int x = i * STRIDE;
int y = j * STRIDE;
for (int k = 0; k < FILTER_SIZE * FILTER_SIZE; k++) {
hInMat2D[idx2(d * FILTER_SIZE * FILTER_SIZE + k, i * in2DSize + j, in2DSize * in2DSize)] = hInMat3D[idx3(d, x + dx[k], y + dy[k], in2DSize)];
}
}
}
}
// kernel3D2Mat2D
for (int k = 0; k < FILTER_NUM; k++) {
for (int d = 0; d < MATRIX_CHANNEL; d++) {
for (int i = 0; i < FILTER_SIZE; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < FILTER_SIZE; j++) {
hKernel2D[idx2(k, (d * FILTER_SIZE * FILTER_SIZE + i * FILTER_SIZE + j), MATRIX_CHANNEL * FILTER_SIZE * FILTER_SIZE)] = hKernel3D[idx3(k, i, j, FILTER_SIZE)];
}
}
}
}
使用 cuDNN 提供的卷积方法进行卷积操作
NVIDIA cuDNN 是用于深度神经网络的 GPU 加速库。它强调性能、易用性和低内存开销。
cuDNN 中计算卷积操作的由cudnnConvolutionForward()来实现,其原型为
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
cudnnStatus_t CUDNNWINAPI cudnnConvolutionForward(
cudnnHandle_t handle,
const void *alpha,
const cudnnTensorDescriptor_t xDesc,
const void *x,
const cudnnFilterDescriptor_t wDesc,
const void *w,
const cudnnConvolutionDescriptor_t convDesc,
cudnnConvolutionFwdAlgo_t algo,
void *workSpace,
size_t workSpaceSizeInBytes,
const void *beta,
const cudnnTensorDescriptor_t yDesc,
void *y );
首先使用库
0
#include <cudnn.h>
然后创建 cudnn 句柄和上下文句柄,然后分别定义输入的张量,卷积核,输出的张量的大小需要使用 cudnnGetConvolution2dForwardOutputDim() 来获得。最后使用 cudnnConvolutionForward() 来完成计算。
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
// Compile: nvcc -I /opt/conda/include/ -L /opt/conda/lib/ -lcudnn cudnn.cu -o cudnn
// Run: export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/opt/conda/lib/
// ./ cudnn
#include <cuda.h>
...
int main() {
...
clock_t startTime = clock();
cudnnStatus_t status;
cudnnHandle_t cudnn_handle;
cudnnCreate(&cudnn_handle);
clock_t startTime2 = clock();
cudnnTensorDescriptor_t matrixDesc;
cudnnCreateTensorDescriptor(&matrixDesc);
cudnnSetTensor4dDescriptor(matrixDesc, CUDNN_TENSOR_NCHW, CUDNN_DATA_FLOAT, 1, MATRIX_CHANNEL, MATRIX_SIZE, MATRIX_SIZE);
float *dInMat;
cudaMalloc(&dInMat, sizeof(float) * MATRIX_CHANNEL * MATRIX_SIZE * MATRIX_SIZE);
cudaMemcpy(dInMat, hInMat, sizeof(float) * MATRIX_CHANNEL * MATRIX_SIZE * MATRIX_SIZE, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudnnFilterDescriptor_t kernelDesc;
cudnnCreateFilterDescriptor(&kernelDesc);
cudnnSetFilter4dDescriptor(kernelDesc, CUDNN_DATA_FLOAT, CUDNN_TENSOR_NCHW, FILTER_NUM, MATRIX_CHANNEL, FILTER_SIZE, FILTER_SIZE);
float *dKernel;
cudaMalloc(&dKernel, sizeof(float) * FILTER_NUM * MATRIX_CHANNEL * FILTER_SIZE * FILTER_SIZE);
cudaMemcpy(dKernel, hKernel, sizeof(float) * FILTER_NUM * MATRIX_CHANNEL * FILTER_SIZE * FILTER_SIZE, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudnnConvolutionDescriptor_t convDesc;
cudnnCreateConvolutionDescriptor(&convDesc);
cudnnSetConvolution2dDescriptor(convDesc, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, CUDNN_CROSS_CORRELATION, CUDNN_DATA_FLOAT);
int outN, outC, outH, outW;
cudnnGetConvolution2dForwardOutputDim(convDesc, matrixDesc, kernelDesc, &outN, &outC, &outH, &outW);
cudnnTensorDescriptor_t outputDesc;
cudnnCreateTensorDescriptor(&outputDesc);
cudnnSetTensor4dDescriptor(outputDesc, CUDNN_TENSOR_NCHW, CUDNN_DATA_FLOAT, outN, outC, outH, outW);
float *dOutMat;
cudaMalloc(&dOutMat, sizeof(float) * outN * outC * outH * outW);
float *hOutMat = (float *)malloc(sizeof(float) * outN * outC * outH * outW);
cudnnConvolutionFwdAlgo_t algo;
cudnnGetConvolutionForwardAlgorithm(cudnn_handle, matrixDesc, kernelDesc, convDesc, outputDesc, CUDNN_CONVOLUTION_FWD_PREFER_FASTEST, 0, &algo);
size_t workspace_size = 0;
cudnnGetConvolutionForwardWorkspaceSize(cudnn_handle, matrixDesc, kernelDesc, convDesc, outputDesc, algo, &workspace_size);
void *workspace;
cudaMalloc(&workspace, workspace_size);
float alpha = 1.0f;
float beta = 0.0f;
status = cudnnConvolutionForward(cudnn_handle, &alpha, matrixDesc, dInMat, kernelDesc, dKernel, convDesc, algo, workspace, workspace_size, &beta, outputDesc, dOutMat);
cudnnDestroy(cudnn_handle);
cudaMemcpy(hOutMat, dOutMat, sizeof(float) * outN * outC * outH * outW, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaFree(dInMat);
cudaFree(dKernel);
cudaFree(dOutMat);
clock_t endTime = clock();
printf("Time cost = %fs (%fs)\n", (float)(endTime - startTime) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC, (float)(endTime - startTime2) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
free(hInMat);
free(hKernel);
free(hOutMat);
return 0;
}
测试发现在构建 cudnn 句柄和上下文句柄的时候耗时十分漫长,计算时间很短。
各种方法的比较
| MatrixSize | Time [CONV] | Time [im2col] | cuDNN |
|---|---|---|---|
| 512 | 0.210600s | 0.200572s | 1.564251s (0.008061s) |
| 1024 | 0.217814s | 0.210927s | 1.382498s (0.018986s) |
| 2048 | 0.225991s | 0.213380s | 1.451955s (0.052267s) |
| 4096 | 0.318341s | 0.292239s | 1.694651s (0.157581s) |
| 8192 | 0.521228s | 0.460625s | 1.945823s (0.685741s) |
im2col 比单纯的 cuda 卷积要快一点点,cuDNN 在申请句柄的时候花了许多时间,但是去除掉这部分时间的话会发现……矩阵规模小的时候很快,矩阵规模变大之后反而变慢了。
References
https://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/54691225
https://blog.csdn.net/sunmc1204953974/article/details/51098028
https://blog.csdn.net/dwyane12138/article/details/78449898
https://cs231n.github.io/convolutional-networks/
https://stanford.edu/~shervine/teaching/cs-230/cheatsheet-convolutional-neural-networks
https://www.jianshu.com/p/3d925c2ef55e
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.