DCS3001 - NLP 2021 Fall
爬取和解析文章
爬取和解析网页 web-crawler-in-python
使用 requests 爬取网页
0
1
2
3
4
5
import requests
url = "https://news.ifeng.com/c/89TNORdIths"
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/63.0.3239.132 Safari/537.36 QIHU 360SE'
}
f = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
这时得到的HTML源码,我们可以通过分析源码得出需要解析的内容的tag。
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
<h1 class="topic-2Eq5D0Zm">推动金砖...重要讲话引发热议</h1>
...
<div class="text-3w2e3DBc">
<p>金...活力。</p>
<p>“通力合作破解公共卫生难题”</p>
...
<p>(本报...9月11日电 记者...邹松)</p>
</div>
在这个网页中我们可以看出 topic-2Eq5D0Zm 类是标题, text-3w2e3DBc 类是正文,正文分为许多段。
使用 BeautifulSoup 解析网页
The BeautifulSoup library has three methods to find elements:
findall(): find all nodes
find(): find a single node
select(): finds according to the selector CSS Selector
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(f.content, 'lxml')
title = soup.find('h1', {'class': 'topic-2Eq5D0Zm'}).string.strip()
content_p = soup.find('div',{'class': 'main_content-28C-Fj2p'}).find_all('p')
content=''
for i in content_p:
content += i.string.strip()
print(url,'\n',title,'\n',content,'\n')
把信息写入到xls文件中
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
from xlwt import *
workbook = Workbook(encoding='utf-8')
table = workbook.add_sheet('data')
table.write(0, 0, 'URL')
table.write(0, 1, 'Title')
table.write(0, 2, 'Content')
line = 1
# 进行上述两项工作
table.write(line, 0, url)
table.write(line, 1, title)
table.write(line, 2, content)
line += 1
workbook.save('raw_text.xls')
使用结巴做中文分词
jieba.cut 方法接受四个输入参数: 需要分词的字符串;cut_all 参数用来控制是否采用全模式;HMM 参数用来控制是否使用 HMM 模型;use_paddle 参数用来控制是否使用paddle模式下的分词模式,paddle模式采用延迟加载方式,通过enable_paddle接口安装paddlepaddle-tiny,并且import相关代码;
jieba.cut_for_search 方法接受两个参数:需要分词的字符串;是否使用 HMM 模型。该方法适合用于搜索引擎构建倒排索引的分词,粒度比较细 待分词的字符串可以是 unicode 或 UTF-8 字符串、GBK 字符串。注意:不建议直接输入 GBK 字符串,可能无法预料地错误解码成 UTF-8
jieba.cut 以及 jieba.cut_for_search 返回的结构都是一个可迭代的 generator,可以使用 for 循环来获得分词后得到的每一个词语(unicode),或者用 jieba.lcut 以及 jieba.lcut_for_search 直接返回 list
jieba.Tokenizer(dictionary=DEFAULT_DICT) 新建自定义分词器,可用于同时使用不同词典。
jieba.dt 为默认分词器,所有全局分词相关函数都是该分词器的映射。
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
import jieba
import xlrd
import xlwt
data = xlrd.open_workbook('raw_text.xls')
table = data.sheet_by_name('data')
url = table.cell_value(1,0)
title = table.cell_value(1,1)
content = table.cell_value(1,2)
title = jieba.cut(title, cut_all = False) # 精确模式
content = jieba.cut(content, cut_all = False) # 精确模式
title = "/".join(title)
content = "/".join(content)
print(title)
print(content)
workbook = xlwt.Workbook(encoding='utf-8')
table = workbook.add_sheet('data')
table.write(0, 0, 'URL')
table.write(0, 1, 'Title')
table.write(0, 2, 'Content')
table.write(1, 0, url)
table.write(1, 1, title)
table.write(1, 2, content)
workbook.save('after_process.xls')
Apply Word2Vec on tokenized sentences
Gensim Word2Vec 的输入可以是可迭代列表,这里可以使用 LineSentence() 来实现文本的转换,输入的文本文件中应该用空格分词。
处理数据
由于之前的分词结果使用 "/" 来分词并且还保留了标点符号,所以我们在训练前先处理数据。
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
from gensim.models import Word2Vec
import gensim
import xlrd
# read data
data = xlrd.open_workbook('hw1/after_process.xls')
table = data.sheet_by_name('data')
url = table.cell_value(1, 0)
title = table.cell_value(1, 1)
content = table.cell_value(1, 2)
# preprocess data
title += '\n' + content
str = title.replace(',', '').replace('。', '\n')\
.replace(',', '').replace('.', '\n')\
.replace('?', '\n').replace('?', '\n')\
.replace('!', '\n').replace('!', '\n')\
.replace('(', '').replace('(', '')\
.replace(')', '').replace(')', '')\
.replace('“', '').replace('”', '').replace('"', '')\
.replace('’', '').replace('‘', '').replace('\'', '')\
.replace('、', '').replace(':', '').replace(':', '')\
.replace('[', '').replace(']', '')\
.replace('{', '').replace('}', '')\
.replace('<', '').replace('>', '')\
.replace('《', '').replace('》', '')\
.replace(';', '').replace(';', '')\
.replace('-', '').replace('_', '')\
.replace('·', '').replace('+', '')\
.replace('…', '').replace('—', '')\
.replace('〗', '').replace('〖', '')\
.replace('/', ' ') # 空格分词 每句一行
fout = open('preprocessed.txt', 'w')
fout.write(str)
fout.close()
使用 gensim.models.word2vec.Word2Vec 训练词向量
部分参数如下:
sentences- 可以是一个List,对于大语料集,建议使用BrownCorpus,Text8Corpus或LineSentence构建。sg- 用于设置训练算法,默认为0,对应CBOW算法;sg=1则采用skip-gram算法。vector_size- 是指输出的词的向量维数,默认为100。大的size需要更多的训练数据,但是效果会更好。推荐值为几十到几百。window- 为训练的窗口大小,8表示每个词考虑前8个词与后8个词(实际代码中还有一个随机选窗口的过程,窗口大小<=5),默认值为5。min_count- 可以对字典做截断. 词频少于min_count次数的单词会被丢弃掉, 默认值为5。workers- 参数控制训练的并行数。epochs- 迭代次数,默认为5。
0
1
2
3
# train
model = Word2Vec(sentences=gensim.models.word2vec.LineSentence(
'preprocessed.txt'), vector_size=120, window=5, min_count=1, workers=4, epochs=28)
model.save("word2vec.model")
输出所有词向量
0
1
2
3
4
fout = open('word_vectors.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
for key in model.wv.index_to_key:
line = key + ':' + str(model.wv[key]) + '\n'
fout.write(line)
fout.close()
输出与 “中国” 最相关的十个词
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
fout = open('word_sims.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
# vector = model.wv['中国'] # get numpy vector of a word
sims = model.wv.most_similar('中国', topn=10) # get other similar words
for sim in sims:
line = str(sim[0])+": "+str(sim[1])+"\n"
fout.write(line)
fout.close()
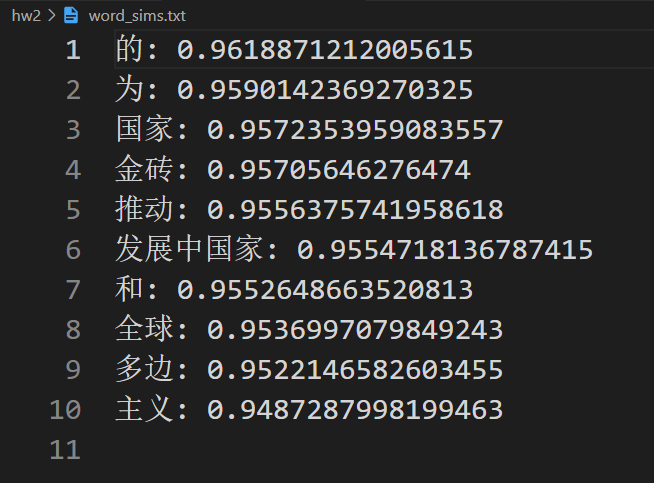
由于样本比较少,训练出来结果一般。
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.